What is Authorization in Medical Billing?
Are your front-office employees wasting more time on hold to insurance companies than attending to patients? If so, you aren’t alone. To most US physicians, the administrative challenge of authorization in medical billing process has evolved from an ordinary check and balance system to a comprehensive revenue cycle bottleneck.
We will go into “what is authorization in healthcare”, what the various types of approvals you should be tracking are, and give you a roadmap to the step-by-step perfect internal workflow. By the time you finish reading this guide, you will have a practical vision of how to eliminate delays in care delivery and avoid the trap of denial. So let’s begin.
What is Authorization Medical Billing?
Fundamentally, authorization in medical billing, commonly known as prior authorization, pre-certification, or pre-authorization, is an obligation by health insurance companies that patients require prior to receiving some medical services. It is just a form of the payer saying, “We agree to this service, it is medically necessary, and all other policy requirements are satisfied.”
It is important to learn, though, that an authorization does not mean payment. It is a tentative affirmation. A claim may be rejected despite a valid medical authorization in case the eligibility of the patient changes or the coding on the claim at the end of the service does not correspond to the authorized service.
This process is a utilization management gatekeeper in the complicated environment of authorization in the US medical systems. It is used by the payers to make sure the treatment plan is evidence-based and directs providers to cheaper alternatives that include generic medicine or cheaper diagnostic centers.
How Authorization Works in Medical Billing?
- It starts when a provider decides the need to undergo a certain treatment or test.
- After the order has been placed, the billing or the administrative team should verify the details of the insurance plan.
- In case prior authorization in medical billing is necessary, the practice sends a request over the portal, fax, or telephone to the payer, attached with clinical notes, lab results, and a letter of medical necessity.
- This data is then compared to the internal standards of the payer medical review team. They will allow the request, put it on hold to seek further details, or reject it.
- In the case of approval, an authorization number is provided, and this has to be carefully documented and attached to the end of the insurance claim.
Why is Authorization Important?
The best means to avoid hard denials is to secure authorization in medical billing. In its absence, the insurance company has a contractual authority to refuse all the payments and usually impose the medical cost on the patient, resulting in low patient satisfaction and poor bad debt on the practice.
What are the Common Services Requiring PA?
Although each payer is unique, in the medical billing process, some high-cost or high-utilization services nearly always need pre-authorization:
- Advanced Imaging: MRI, CT scans, and PET scans.
- Inpatient Stays: Scheduled surgeries and hospital admissions.
- Specialty Medications: Biologics, chemotherapy, and high-cost injectable drugs.
- Durable Medical Equipment (DME): CPAP machines, custom wheelchairs, and prosthetics.
- Genetic Testing: Complex molecular diagnostics.
- Therapy Services: Extended physical, occupational, or speech therapy.
Are There Any Challenges in Authorization?
The problems are obvious and increasing. In the 2024 AMA Prior Authorization Physician Survey, 93% of doctors stated that patient care is delayed as a result of the authorization process.
Common hurdles include:
- Inconsistent Rules: What BlueCross needs may have no similarity with Aetna or UnitedHealthcare.
- Delays: The delays during payer response (7-14 days) may compromise patient health.
- Clinical Subjectivity: Payors might object to a clinical judgment by a physician of the medical necessity.
- Manual Workflows: The use of manual processes, such as the use of outdated fax machines or slow portals, is still common among most payers who do not connect with EHRs.
What are the Different Steps in Medical Billing Authorization?
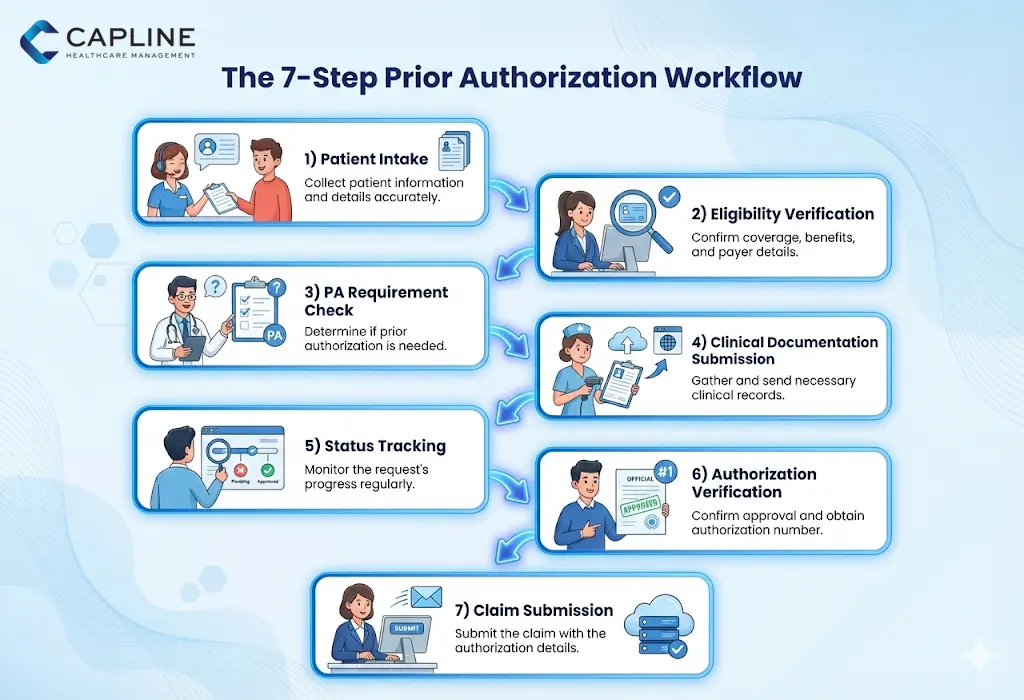
To assist you in streamlining your operations, we have described the conventional seven-step operation that most prosperous practices apply.
Step 1: Patient Scheduling and Intake
The process starts here. Gather the correct insurance data and check patient identity. Make sure that a clinical reason for the visit is well recorded in the EHR.
Step 2: Benefit and Eligibility Checking
Before seeking authorization, you have to check the coverage of the patient. Is the proposed service based on the plan? Is insurance still in force?
Pro Tip: Have [Eligibility Verification Services] automate this and pick up the slackers of the policies even before the patient steps through the door.
Step 3: Determining Authorization Requirements
Use the payer’s portal or a clearinghouse tool to check if the specific CPT code (procedure code) requires medical authorization. Never assume because rules change quarterly.
Step 4: Submission of Clinical Documentation
This is where most denials are born. You must provide the “why.” This includes:
- Recent office visit notes.
- Failure of “conservative” treatments (e.g., physical therapy before surgery).
- Relevant lab or imaging results.
- A clear diagnosis (ICD-10 code) that matches the requested CPT.
Step 5: Status Tracking and Follow-Up
Do not wait to see a letter in the mail. Have an employee verify the pending prior authorization in the medical billing request every 48 hours. In case one request is pended, supply the missing information as soon as possible.
Step 6: Receipt and Verification
Once you receive the authorization, verify the details:
- Is the date of service (DOS) within the approved window?
- Does the CPT code match exactly what you intend to bill?
- Is the “rendering provider” listed correctly?
Step 7: Claim Submission
When the bill is sent, the authorization number must be placed in the correct box (typically Box 23 on the CMS-1500 form). If this number is missing or typoed, the claim will be rejected instantly.
Conclusion
Mastering authorization in medical billing is a reality of today. By implementing a standardized 7-step workflow and staying ahead of payer requirements, you can significantly reduce your denial rates and improve patient outcomes.
Don’t let administrative red tape stand between you and your revenue. Start optimizing your authorization in healthcare today with Capline. Call us now!
People Also Ask About Medical Billing Authorization
1. What are the key terms in medical billing authorization?
The key ones are prior authorization (pre-service approval), medical necessity (the clinical justification of care), and CPT codes (the exact procedures that are being authorized).
2. What is the authorization process?
The authorization process consists of checking the insurance of a patient, finding out whether a certain service is something that the payer needs to provide a thumbs up, providing clinical evidence to back the request, and tracking the request until the payment is confirmed by an approval number.
3. What is authorization in RCM?
Authorization is a front office activity in Revenue Cycle Management (RCM), which makes sure that a claim is given a proper approval number before being submitted. I
4. What services most commonly require prior authorization?
The most common are high-cost services like MRIs, CT scans, inpatient surgery, and specialty injectable drugs. Genetic testing and some outpatient treatments have also recently been included in the list of authorized services to be paid for in the healthcare sector by the payers.
5. What are common prior authorization denial reasons?
The most common include lack of medical necessity, incomplete clinical documentation, or merely seeking the authorization after the service has been delivered.
6. What role does clinical documentation play in PA success?
The payers must observe that you have adhered to step therapy procedures and that the patient has a condition that suits his or her special requirements for the treatment requested.
7. When can providers bill without prior authorization?
The providers are usually allowed to bill without PA in the case of actual emergencies (EMTALA and No Surprises Act).



