What are the Differences Between PPO & HMO Insurances?
PPO vs HMO is a common choice that arises in the minds of patients. Being a provider or a practice administrator, you face the reality of these differences daily.
You feel it at the front desk when a patient is in the office and realizes he is not covered, and you feel it at the billing department when they are denied claims because they lack referrals. This patient’s problem is not only confusing to you but also has a direct effect on your practice’s workflow, revenue cycle, and timely care delivery.
We are going to deconstruct the HMO vs PPO insurance in this blog. Regardless of whether you are assisting a patient in picking a plan at open enrollment or in your billing department handling denials, being aware of these differences can save time, reduce frustration, and enhance patient satisfaction. Let’s dive in.
What is a PPO Plan?
A preferred provider organization, or PPO, health plan is considered to be one of the most popular health insurance plans in the US. It is flexible, as it enables the patient to access providers within the plan as well as out of the network.
Key features of PPO plans:
- No necessity to have a primary care physician (PCP) referral in order to visit specialists.
- Out-of-network care (at higher costs) coverage.
- Greater provider networks, which can be of a national scale.
- Increased premiums and deductibles than in other plans.
The Kaiser Family Foundation (2024) Employer Health Benefits Survey indicates that roughly 48 percent of covered employees were enrolled in PPO plans, which is the most prevalent employer-sponsored insurance of the survey.
What is an HMO Plan?
The full form of HMO is Health Maintenance Organization. It is a health insurance plan that requires every person enrolled in the plan to choose a primary care doctor. The selected primary care doctor is responsible for referring the patient to in-network specialists according to requirements. Each HMO plan covers a few health specialists who agree to provide medical services at the best rates based on discussions with insurance providers.
Usually, the benefits of HMO plans are location-based. Some of the key benefits of HMO plans are
- Low monthly premiums
- Affordable out-of-pocket fees
- Low consultation charges
- Complete care of your health by your primary physician
- Easy settlement of claims.
What are the Differences Between PPO and HMO Health Care Plans?
In the comparison of PPO vs HMO, the essential differences reduce to flexibility, costs, provider network, and requirements of referrals. These factors directly affect the access of patients to your services and the revenue cycle of your practice as a provider.
Here’s a detailed breakdown:
1. Costs
HMOs generally have reduced monthly payments and out-of-pocket costs. As an example, employer-sponsored PPO plans in many cases have higher average premiums compared to HMOs; this is due to the increased flexibility. Based on recent KFF reports, using 2024-2025 surveys, PPO enrollees must pay more in general, which could affect patient choices in high-deductible plans.
2. Referrals and Care Coordination
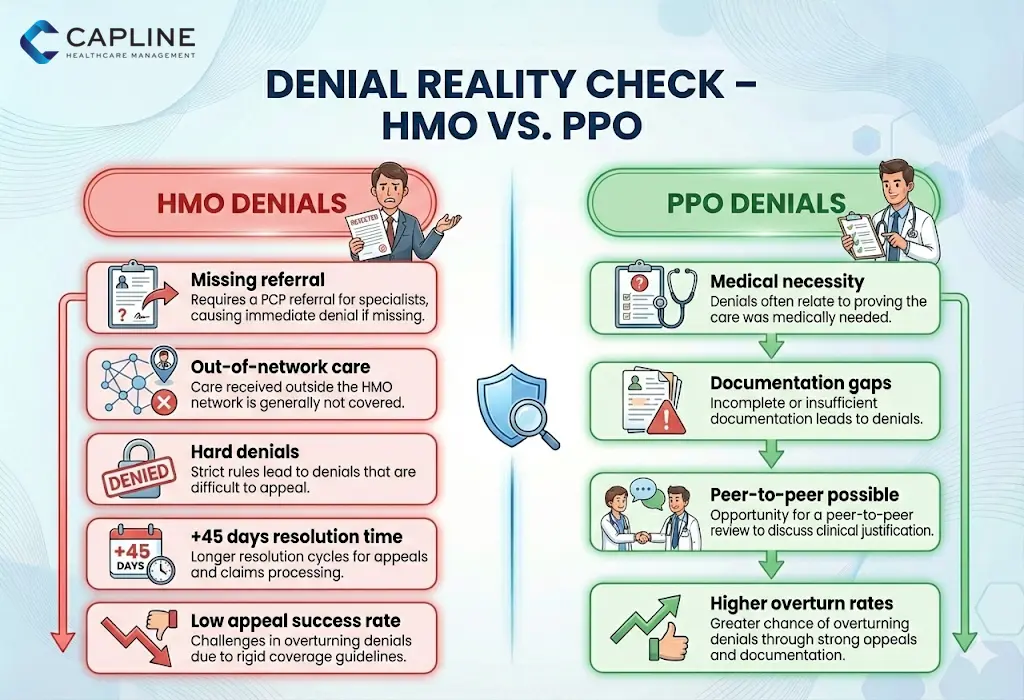
HMO: Specialists require referrals from PCP. In this type of gatekeeper model, preventive care is encouraged but may postpone access.
PPO: No referrals are necessary; patients are able to refer themselves to specialists, making the care more fast, yet it may increase utilization.
Patients with long-term illnesses tend to go to PPOs because they do not have to face the hurdle of referrals.
3. Networks and Choice of Providers
HMO: Smaller, local networks. Patients will be required to remain within the network or pay the full price (except in the case of emergencies).
PPO: Larger networks but partially out-of-network. Best suited to patients who are on the move or second opinion.
Provider networks consist of contracted physicians, hospitals, and facilities (more in the FAQ).
4. Out-of-Network Coverage
This is the primary difference between HMO and PPO: the former offers virtually none, whereas the latter offers some (typically 60-80 percent with increased deductibles).
When a large number of HMO patients do not have your practice as in-network, then you might get fewer referrals. You can consider this: Credentialing and Network Enrollment Services from Capline
Should I Get an HMO or a PPO Plan?
PPO or HMO, which is the better choice, is determined by the needs of a patient. HMOs are beneficial to healthy individuals due to the need for fewer costs and coordinated care. PPOs are more suitable for individuals who require specialist access or flexibility.
Quick summary:
- Select an HMO because it is cheaper and preventive-oriented.
- Go with PPO because it will be convenient.
Nonetheless, HMOs are also a good value to low-cost patients who do not require specialist care frequently.
How to Choose the Best One Between PPO and HMO?
They are both different in their own ways. Here is a practical checklist for practices on how to discuss with a patient:
- Determine health requirements: Routine experts? – PPO.
- Budget priorities: More low premiums? – HMO.
- Preferences of providers: Desire to retain existing physicians? Check networks.
- Frequency of travel: Requirement of out-of-area care? – PPO.
- Family: Do you have kids or the older generation with special needs? Lean PPO.
Educate patients to check summaries of benefits at open enrollment.
Conclusion
Knowledge of PPO vs HMO will enable us as providers to be more knowledgeable to lead patients, enhance adherence, and maximize billing. PPOs are more flexible, and HMOs are more effective in managing costs, although the most appropriate option is dependent on the situation of the specific patient.
We have been helping practices similar to yours at Capline to overcome insurance challenges to facilitate a smoother operation. Are you willing to optimize your billing or patient advising? Get in touch with us and have a consultation.
FAQs
1. What are the drawbacks of an HMO?
HMOs limit provider choice to in-network only, require PCP referrals (which can delay care), and offer no out-of-network coverage except emergencies. This restricted access can frustrate patients needing specialized or immediate care.
2. Which plan, HMO or PPO, offers more flexibility?
PPO plans offer significantly more flexibility, allowing direct specialist access without referrals and partial coverage for out-of-network providers. HMOs prioritize coordination over choice.
3. What are the 4 levels of coverage?
In marketplace plans, the four metal levels are Bronze (lowest premiums, highest costs), Silver, Gold, and Platinum (highest premiums, lowest out-of-pocket). These apply across HMO and PPO types.
4. What are the disadvantages of a PPO plan?
PPOs have higher premiums and deductibles, plus increased out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network care. Patients may also face more administrative complexity with claims.
5. Can we claim 100% medical insurance?
No plan covers 100% of all medical costs indefinitely; most have deductibles, copays, coinsurance, and out-of-pocket maximums. After meeting limits, coverage can reach near 100% for in-network services.
6. What are provider networks?
Provider networks are groups of doctors, hospitals, and facilities contracted with an insurer to provide services at negotiated rates. Staying in-network lowers patient costs.
7. What is the difference between in-network and out-of-network?
In-network providers have agreed rates with the insurer, resulting in lower patient costs. Out-of-network means no contract, leading to higher bills or no coverage (especially in HMOs).
8. Do doctors prefer HMO or PPO?
Many doctors and practices prefer PPOs due to broader patient pools, fewer referral requirements, and potentially higher reimbursements. However, HMOs can provide steady referrals through coordinated care.



